Genome Search Plotter
A Robust Method for Finding the Automated Best Matched Genes Based on Grouping Similar Fragments of Large-Scale References for Genome Assembly
Big data research on genomic sequence analysis has accelerated considerably with the development of next-generation sequencing. Currently, research on genomic sequencing has been conducted using various methods, ranging from the assembly of reads consisting of fragments to the annotation of genetic information using a database that contains known genome information. According to the development, most tools to analyze the new organelles’ genetic information requires different input formats such as FASTA, GeneBank (GB) and tab separated files. The various data formats should be modified to satisfy the requirements of the gene annotation system after genome assembly. In addition, the currently available tools for the analysis of organelles are usually developed only for specific organisms, thus the need for gene prediction tools, which are useful for any organism, has been increased. The proposed method—termed the genome_search_plotter—is designed for the easy analysis of genome information from the related references without any file format modification. Anyone who is interested in intracellular organelles such as the nucleus, chloroplast, and mitochondria can analyze the genetic information using the assembled contig of an unknown genome and a reference model without any modification of the data from the assembled contig.
https://bigdata.dongguk.edu/gene_project/genome_search_plotter
Input
Reference accesion Number:
- In order to run the BLAST with query contigs and reference, Reference sequences are required. For more information, please refer to NCBI site
Input File Format:
- Input file is the assembled contigs and format should be in FASTA format. The number of contigs are not limimted, but, it will takes several hours. We recommend to copy the reslut page URL for your reference.
Maximum number of matched BLAST hit group:
- The number sets the maximum groups which is based on the BLAST result.
Minimum number of matched sub gene’s count per each contig:
- Please refer to below Figure 1-B.
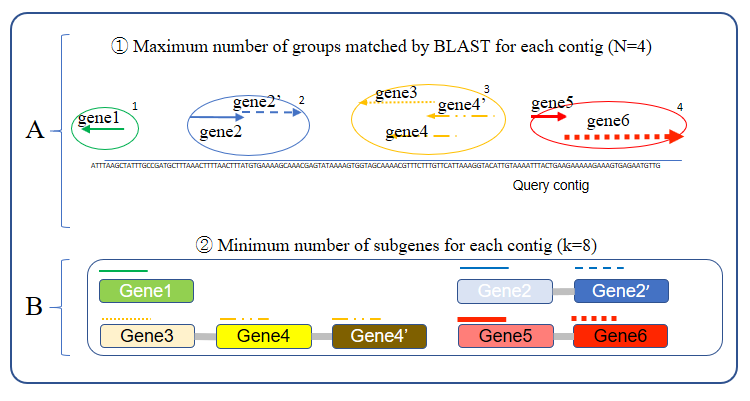
Figure 1. Maximum number of hit group and mininum number of subgene’s count
Output
The provided files are “sorted sequences” and “PDF” files
Sorted by the number of subgene:
- BLAST result file which is sorted by BLAST e-value. In the sorted query sequences file, sequences are sorted by the number of matched sub-genes and the sequences that do not meet the minimum value of k are filtered out
PDF file:
- The results are shown as a graph depicting matches with the 149 reference genomes on the X-axis and query sequences uploaded by the user on the Y-axis. Each 150 line on the plot indicates that a query contig is matched with the reference sequences.